Machine-made rugs are one of the most widely used flooring solutions in today’s global market, valued for their consistency, scalability, and cost efficiency. Unlike handmade rugs, which rely heavily on manual labor and long production times, machine-made rugs are produced through advanced industrial processes that allow precise control over design, materials, and quality. As a result, they play a central role in residential, commercial, and large-scale project applications worldwide.
Understanding how machine-made rugs are produced is especially important for buyers, wholesalers, and retailers. For buyers, knowledge of materials and manufacturing methods helps in choosing rugs that match their needs in terms of durability, comfort, and price. For wholesalers and retailers, insight into the production process enables better product comparison, clearer communication with customers, and more informed sourcing decisions. It also reduces the risk of misjudging quality based solely on appearance or price.
In this guide, we take a step-by-step look at the complete journey of a machine-made rug—from raw yarn selection to the finished product ready for global distribution. You will learn how different materials are prepared, how modern weaving technologies work, and which finishing and quality control processes determine the final performance of a rug. By the end of this article, you will have a clear, practical understanding of what truly defines a high-quality machine-made rug.
What Are Machine-Made Rugs?
Machine-made rugs—also known as machine woven rugs or factory-made rugs—are rugs produced using automated looms and industrial weaving technologies. Unlike traditional rugs that are hand-knotted or hand-woven, these rugs are manufactured in controlled factory environments where materials, patterns, and dimensions are precisely managed. This industrial rug manufacturing process enables high consistency, repeatable designs, and efficient large-scale production.
How Machine-Made Rugs Differ from Handmade Rugs
- Production method: Machine-made rugs are created on power looms (e.g., Wilton, Axminster, Jacquard), while handmade rugs rely on manual labor and artisanal techniques.
- Consistency: Factory-made rugs deliver uniform density, pile height, and pattern accuracy across batches; handmade rugs can vary from piece to piece.
- Time & cost: Automated production significantly reduces lead time and cost, making machine-made rugs more accessible for broader markets.
- Design flexibility: Digital design transfer allows complex, repeatable patterns at scale, whereas handmade designs depend on artisan skill and time.
Common Applications of Machine-Made Rugs
- Residential use: Living rooms, bedrooms, and dining areas where durability and affordability are key.
- Commercial spaces: Offices, retail stores, and public buildings requiring consistent quality and easy replacement.
- Hospitality projects: Hotels, resorts, and serviced apartments that need bulk quantities with standardized specifications.
- Export markets: Ideal for global distribution due to scalable production, stable quality, and competitive pricing.
In short, machine-made rugs combine industrial efficiency with modern design capabilities, making them a practical solution for both everyday use and large-scale projects.
Raw Materials Used in Machine-Made Rugs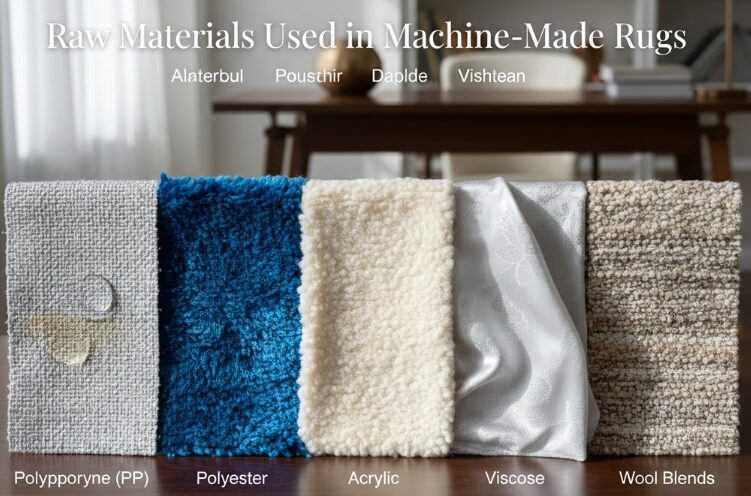
The quality and performance of a machine-made rug largely depend on the raw materials, especially the type of yarn used. Each yarn has distinct characteristics that affect durability, appearance, comfort, and price. Understanding these materials helps buyers and professionals choose the right rug for specific applications.
Types of Yarn Used
Polypropylene (PP)
Polypropylene is one of the most common materials used in machine-made rugs. It is lightweight, moisture-resistant, and highly cost-effective. PP yarns are known for their resistance to stains and fading, making them suitable for high-traffic areas and outdoor or semi-outdoor use. However, they are generally less soft and less heat-resistant compared to other fibers.
Polyester
Polyester yarns are valued for their softness and vibrant color appearance. They offer excellent color clarity and a silky texture, which makes them popular for decorative and modern rug designs. While polyester rugs are visually appealing and affordable, they are typically less durable than polypropylene or wool in very high-traffic environments.
Acrylic
Acrylic is often used as a synthetic alternative to wool because of its soft feel and warm appearance. It provides good color retention and a pleasant texture underfoot. Acrylic rugs tend to be more expensive than PP or polyester rugs but still more affordable than pure wool options. They are suitable for residential spaces where comfort is a priority.
Viscose
Viscose, sometimes referred to as artificial silk, is used primarily for its luxurious sheen and smooth texture. It enhances the visual depth of patterns and adds an elegant finish to rugs. However, viscose is less durable and more sensitive to moisture, which makes it better suited for low-traffic areas or decorative purposes.
Wool Blends
Wool blends combine natural wool fibers with synthetic yarns such as polyester or polypropylene. This combination balances comfort, durability, and cost. Wool contributes natural softness, insulation, and resilience, while synthetic fibers improve strength and reduce overall price. Wool-blend rugs are often positioned as premium machine-made products.
How Yarn Quality Affects Rug Performance

Durability
Higher-quality yarns with proper spinning and heat-setting last longer and maintain their structure under daily use. Materials like polypropylene and wool blends generally perform better in high-traffic areas.
Softness
Yarn type and finishing processes directly affect how a rug feels underfoot. Acrylic, polyester, and viscose offer greater softness, while PP tends to feel firmer.
Color Retention
Solution-dyed and high-quality synthetic yarns retain color better over time and resist fading caused by sunlight or cleaning. Poor-quality yarns may lose vibrancy quickly.
Price Impact
Raw material choice is a major factor in rug pricing. Polypropylene rugs are typically the most affordable, while viscose and wool-blend rugs fall into higher price ranges due to material cost and finishing requirements.
In summary, selecting the right yarn is a critical step in machine-made rug production, as it directly determines the rug’s performance, appearance, lifespan, and market positioning.
Yarn Preparation Process
Before weaving begins, raw fibers must be carefully prepared to ensure the yarn performs well during production and in everyday use. The yarn preparation stage plays a critical role in determining a machine-made rug’s strength, texture, appearance, and longevity.
Spinning and Twisting
Spinning is the process of converting raw fibers—synthetic or natural—into continuous yarn. During spinning, fibers are drawn out and aligned to create a uniform strand with controlled thickness. Consistency at this stage is essential, as uneven yarn can lead to weak spots, visual defects, or irregular pile height in the final rug.
Twisting follows spinning and involves rotating the yarn strands around their axis. This step significantly affects yarn performance.
Why twist level matters:
- Low twist:
- Softer feel
- More volume and plush appearance
- Lower resistance to abrasion
- High twist:
- Stronger and more durable yarn
- Better resistance to crushing and wear
- Slightly firmer texture
Manufacturers choose the twist level based on the rug’s intended use. For example, high-traffic rugs require tighter twists, while decorative rugs prioritize softness and visual appeal.
Heat-Setting the Yarn
Heat-setting is a thermal process applied mainly to synthetic yarns such as polypropylene, polyester, and acrylic. The yarn is exposed to controlled heat (often using steam or hot air), which stabilizes its molecular structure.
What heat-setting does:
- Locks the twist into the yarn
- Fixes the yarn’s shape and memory
- Improves dimensional stability during weaving and use
Key benefits of heat-set yarns:
- Shape retention: Yarn maintains its form under pressure and daily foot traffic
- Improved softness: Heat relaxes the fibers, resulting in a smoother, more comfortable feel
- Reduced shedding: Loose fibers are minimized, leading to cleaner rugs and less maintenance
- Enhanced appearance: Patterns appear sharper and more defined
Heat-setting is considered a quality indicator in machine-made rugs, as untreated yarns tend to flatten faster and show signs of wear sooner.
Overall, proper spinning, twisting, and heat-setting transform raw fibers into high-performance yarns, ensuring that machine-made rugs meet both functional and aesthetic expectations.
Dyeing and Color Development
The visual appeal of a machine-made rug depends heavily on dyeing and color development. This stage not only determines the rug’s final look but also affects durability, color retention, and how well the rug complements interior spaces.
Solution-Dyed vs. Space-Dyed Yarns
Solution-dyed yarns are created by adding pigments directly to the polymer before the fiber is extruded. This method ensures that the color is fully integrated into the yarn, providing:
- Exceptional colorfastness
- Resistance to fading from sunlight, cleaning, and moisture
- Uniform color across the rug, ideal for high-traffic areas
Space-dyed yarns, on the other hand, are dyed after the fibers are produced, often in multiple colors along the strand. This technique creates:
- Variegated patterns and multi-tonal effects
- Enhanced visual depth and texture in the rug
- Opportunities for creative, modern designs that mimic hand-dyed aesthetics
Choosing between solution-dyed and space-dyed yarns depends on the desired combination of durability and visual style.
Colorfastness and Long-Term Appearance
A rug’s color should maintain its vibrancy for years, despite exposure to sunlight, foot traffic, and routine cleaning. High-quality machine-made rugs undergo rigorous testing for:
- UV resistance: Prevents fading in sunlit rooms
- Bleeding resistance: Ensures colors don’t transfer when cleaned
- Abrasion resistance: Protects patterns from wearing off in high-traffic zones
Rugs made with poorly dyed yarns may show uneven fading, dullness, or color bleeding, affecting both appearance and perceived quality.
How Color Trends Influence Rug Design
Modern machine-made rugs are designed not only for durability but also to align with interior design trends. Manufacturers consider:
- Popular color palettes in home décor
- Seasonal trends and fashion cycles
- Customer preferences in global markets
By combining durable dyeing techniques with contemporary design insights, factories produce rugs that are both long-lasting and visually appealing. This synergy of technology and design ensures that machine-made rugs can meet aesthetic expectations while retaining performance over time.
Weaving Technology in Machine-Made Rugs
The weaving stage is where prepared yarns are transformed into a finished rug with structure, pattern, and texture. Modern machine-made rug production relies on advanced looms and precise control over weaving density and pile height, which together determine the rug’s durability, comfort, and visual appeal.
Types of Weaving Machines
Wilton Looms
Wilton looms are widely used for producing rugs with intricate patterns and dense piles. They are capable of weaving complex designs by controlling each warp thread individually. Wilton machine-made rugs are known for:
- High durability
- Uniform pile height
- Ability to replicate detailed designs similar to hand-knotted rugs
Axminster Looms
Axminster looms are designed for high-speed production while maintaining flexibility in pattern creation. They are ideal for producing rugs with vibrant, multicolored designs. Key features include:
- Precision in pattern transfer
- Ability to use multiple yarn colors simultaneously
- Suitable for both medium- and high-volume production
Jacquard Weaving Systems
Jacquard looms automate complex pattern weaving by using punched cards or digital controls. They allow:
- Highly detailed and repeatable designs
- Combination of various yarn types and colors
- Efficient production of decorative rugs at scale
Each type of loom offers a balance between production speed, design complexity, and cost, enabling manufacturers to cater to different market needs.
Weaving Density and Pile Height
Face Density Explained
Face density refers to the number of yarn tufts per unit area of the rug. Higher face density generally means:
- Greater durability
- Enhanced pattern clarity
- Better resistance to wear and foot traffic
Pile Height and Its Impact
Pile height is the length of the yarn tufts extending from the rug backing. Its selection affects both comfort and functionality:
- Low pile rugs: Firmer underfoot, easier to clean, ideal for high-traffic areas
- Medium pile rugs: Balanced comfort and durability, suitable for most residential spaces
- High pile rugs: Soft, plush texture for luxurious feel, but require more maintenance and are less suitable for heavy-traffic zones
By carefully adjusting weaving density and pile height, manufacturers ensure that machine-made rugs meet both practical performance standards and aesthetic expectations.
Design Transfer and Pattern Creation

One of the key advantages of machine-made rugs is the ability to replicate intricate designs with precision. This is achieved through a combination of digital design tools and advanced weaving technology, ensuring that every rug meets exact specifications.
Digital Rug Design Process
Modern rug manufacturers begin with a digital design workflow. Designers create patterns using specialized software that translates colors, textures, and motifs into a format suitable for automated weaving. This approach allows:
- Easy modification and testing of patterns before production
- Accurate color matching and gradient simulation
- Rapid iteration to respond to market trends and customer preferences
Digital design eliminates many of the inconsistencies associated with manual patterning, ensuring that each rug matches the intended aesthetic.
Pattern Mapping to Weaving Machines
Once the digital design is finalized, it is mapped onto the loom using computer-controlled systems. Each warp and weft thread is assigned a specific color and position according to the pattern. This mapping process ensures:
- Accurate alignment of intricate motifs
- Consistent reproduction across multiple rugs
- Efficient use of materials and yarns
Advanced looms, such as Jacquard and Axminster machines, interpret these digital patterns directly, automating the complex weaving process.
Precision and Repeatability Advantages
The combination of digital design and machine-controlled weaving provides several benefits:
- High precision: Even the smallest details are consistently reproduced
- Repeatability: Large batches of rugs can be produced with identical patterns
- Reduced errors: Minimizes defects that might occur in manual processes
- Scalability: Enables manufacturers to meet bulk orders without compromising quality
This system allows machine-made rugs to offer both design complexity and uniform quality, making them suitable for commercial projects, hospitality spaces, and export markets where consistency is critical.
Finishing Processes After Weaving
After weaving is complete, machine-made rugs undergo finishing processes that refine their texture, enhance durability, and prepare them for use or sale. These steps ensure the rug not only looks polished but also performs well in everyday settings.
Shearing and Surface Finishing
Shearing is the process of trimming the rug’s pile to a uniform height. This step is crucial for:
- Achieving uniform pile height: Ensures the rug has a smooth, even surface, enhancing comfort and aesthetic appeal.
- Enhancing texture and clarity: Highlights patterns and designs, making motifs more defined and visually appealing.
Surface finishing may also include brushing, steaming, or mechanical treatments that soften the fibers, reduce shedding, and create a consistent feel across the entire rug.
Backing and Edge Binding
Latex Backing
Most machine-made rugs are applied with a layer of latex on the backside. This provides:
- Added stability and strength
- Prevention of unraveling or distortion of the weave
- Better adhesion when used with rug pads, preventing slipping
Overlocking and Binding Edges
The edges of the rug are carefully finished with overlocking or binding threads to:
- Protect against fraying
- Maintain the rug’s shape over time
- Provide a neat, professional appearance suitable for both residential and commercial use
These finishing processes transform a raw woven rug into a ready-to-use product, combining durability, visual appeal, and comfort, making it suitable for homes, offices, hotels, and other high-traffic environments.
Quality Control in Rug Manufacturing
Quality control is a critical step in machine-made rug production, ensuring that each rug meets performance, durability, and aesthetic standards before reaching the market. Factories employ rigorous inspections and standardized protocols to maintain consistent product quality.
Inspection Criteria
Machine-made rugs are checked for multiple factors during and after production:
- Knot and tuft consistency: Even in machine-made rugs, the uniformity of loops or cut piles is essential for durability and appearance.
- Density verification: Ensures the correct number of tufts per square inch, which affects longevity, feel, and pattern clarity.
- Color accuracy: Confirms that the rug matches the approved design and dye specifications, maintaining consistent visual appeal across batches.
These inspections often combine automated scanners with human oversight to detect subtle inconsistencies or defects.
International Quality Standards
Top manufacturers adhere to recognized quality standards to guarantee reliability and customer satisfaction:
- ISO 9001: Quality management systems for consistent manufacturing processes.
- Oeko-Tex Standard 100: Ensures rugs are free from harmful chemicals and safe for use in homes and public spaces.
- ANSI/ISO test methods: Standardized testing for durability, abrasion resistance, and colorfastness.
Compliance with these standards ensures machine-made rugs are suitable for both domestic and global markets.
Common Defects and How Factories Prevent Them
Even in industrial production, defects can occur. Common issues include:
- Uneven pile height or density: Prevented through precise loom calibration and routine checks.
- Color inconsistencies: Minimized by strict dyeing protocols and color-matching verification before weaving.
- Loose backing or frayed edges: Addressed by proper latex application and secure edge binding during finishing.
By implementing systematic inspections and corrective measures, factories can consistently produce high-quality rugs that meet customer expectations and perform reliably in real-world conditions.
Quality Control in Rug Manufacturing
Quality control is a critical step in machine-made rug production, ensuring that each rug meets performance, durability, and aesthetic standards before reaching the market. At Rug Legacy, our factories implement rigorous inspections and standardized protocols to maintain consistent high-quality products for both domestic and international buyers.
Inspection Criteria
In our factories, machine-made rugs are checked for multiple factors during and after production:
- Knot and tuft consistency: Even in machine-made rugs, uniform loops or cut piles are essential for durability and appearance.
- Density verification: Ensures the correct number of tufts per square inch, affecting longevity, feel, and pattern clarity.
- Color accuracy: Confirms that each rug matches the approved design and dye specifications, maintaining consistent visual appeal across batches.
Our inspections combine advanced scanning technology with skilled human oversight to catch even subtle inconsistencies or defects.
International Quality Standards
Rug Legacy adheres to recognized international standards to guarantee reliability and customer satisfaction:
- ISO 9001: Ensures quality management systems are in place for consistent manufacturing.
- Oeko-Tex Standard 100: Confirms our rugs are free from harmful chemicals and safe for homes and public spaces.
- ANSI/ISO test methods: Standardized testing for durability, abrasion resistance, and colorfastness.
Compliance with these standards allows Rug Legacy rugs to meet the requirements of both domestic clients and global export markets.
Common Defects and How Our Factories Prevent Them
Even with industrial production, defects can occur. Common issues include:
- Uneven pile height or density: Prevented through precise loom calibration and routine checks.
- Color inconsistencies: Minimized by strict dyeing protocols and color-matching verification before weaving.
- Loose backing or frayed edges: Addressed by proper latex application and secure edge binding during finishing.
By following systematic inspections and corrective measures, our factories ensure Rug Legacy produces high-quality rugs that consistently meet customer expectations and perform reliably in real-world conditions.
Packaging and Global Distribution
Once machine-made rugs have passed quality control, they move on to packaging and distribution, which is essential for protecting the product during transit and ensuring it arrives in perfect condition to customers worldwide.
Rolling and Wrapping Rugs
Rugs are typically rolled rather than folded to prevent creases and damage to the pile. Protective measures include:
- Plastic wrapping or shrink film: Shields the rug from dust, moisture, and minor abrasions.
- Cardboard tubes or corner protectors: Provide extra rigidity, preventing bending or crushing during transport.
- Labeling: Includes product specifications, dimensions, design code, and care instructions, which simplifies inventory management for wholesalers and retailers.
Export Packaging Standards
For international shipments, packaging must meet specific standards to comply with customs regulations and minimize risk during long-distance transport:
- Durable outer packaging: Corrugated boxes or reinforced wrapping to withstand handling and stacking.
- Moisture and pest protection: Prevents mold, mildew, or insect damage, especially for natural fiber or wool-blend rugs.
- Bulk packaging for B2B orders: Large quantities are often palletized and wrapped securely to facilitate shipping efficiency and reduce handling damage.
Logistics Considerations for International Shipping
Efficient logistics are key to ensuring timely delivery and maintaining product quality:
- Transportation mode selection: Air freight for urgent deliveries, sea freight for bulk shipments.
- Customs documentation: Accurate product descriptions, HS codes, and origin certificates prevent delays at international borders.
- Tracking and insurance: Provides buyers with shipment visibility and protects against potential damage or loss during transit.
By combining careful rolling, secure packaging, and optimized logistics, manufacturers ensure that machine-made rugs reach global markets in excellent condition, ready for display or use in homes, offices, and hospitality projects.
Advantages of Machine-Made Rugs
Machine-made rugs offer several key benefits that make them a popular choice for homes, commercial spaces, and large-scale projects. Their combination of technology, efficiency, and design flexibility sets them apart from handmade alternatives.
Consistent Quality
Because machine-made rugs are produced using automated looms and standardized processes, every rug maintains uniform pile height, density, and pattern accuracy. This consistency ensures that customers receive the same high-quality product every time, making them ideal for bulk purchases or large projects where uniform appearance is crucial.
Cost Efficiency
Automated production significantly reduces labor costs and production time compared to handmade rugs. This efficiency translates to more affordable prices without sacrificing basic durability or visual appeal. As a result, machine-made rugs are accessible to a wider audience and suitable for both residential and commercial budgets.
Scalability for Large Projects
Machine production allows manufacturers to produce large quantities of rugs quickly while maintaining uniform design and quality. This makes machine-made rugs ideal for hotels, offices, retail chains, and export markets where consistency across multiple units is essential.
Faster Production Timelines
With advanced looms and digital design integration, machine-made rugs can be produced much faster than handmade options. From raw yarn to finished product, the streamlined process allows manufacturers to respond quickly to market demand, seasonal trends, and bulk orders without compromising quality.
Overall, these advantages make machine-made rugs a practical, reliable, and versatile choice for a wide range of applications, combining quality, affordability, and design flexibility in one product.
Machine-Made Rugs vs. Handmade Rugs
When deciding between machine-made and handmade rugs, it’s important to understand the differences in production, cost, design, and scalability. Each type has its own advantages, and the right choice depends on the buyer’s needs, budget, and intended use.
Feature | Machine-Made Rugs | Handmade Rugs |
Production Speed | Fast | Slow; requires skilled labor and weeks or months per rug |
Price Range | Affordable; suitable for mass-market buyers | Premium; higher cost due to labor and craftsmanship |
Design Consistency | High; identical rugs can be produced in large quantities | Variable; each rug is unique, slight differences in pattern and texture |
Scalability | Excellent; ideal for commercial projects, hotels, or export | Limited; producing large quantities is time-consuming and labor-intensive |
Key Takeaways:
- Machine-made rugs excel in efficiency, repeatability, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for large-scale or commercial applications.
- Handmade rugs offer unique craftsmanship and premium aesthetics, appealing to collectors or buyers seeking artisanal quality.
- Buyers should weigh factors like budget, intended use, and quantity requirements when choosing between the two types.
This comparison helps clarify why machine-made rugs dominate the mass market, while handmade rugs remain a niche for luxury and bespoke projects.
Considerations for Wholesalers and Export Buyers
If you are sourcing rugs for bulk orders, commercial projects, or international markets, it’s important to focus on specifications that meet global standards:
- Compliance with international quality certifications (ISO 9001, Oeko-Tex Standard 100) ensures safety and reliability for export.
- Consistent pattern and color replication across multiple units is crucial for large-scale or hospitality projects.
- Durable packaging and logistics readiness guarantee that rugs arrive intact and ready for sale in different countries.
By keeping these considerations in mind, wholesalers and export buyers can confidently select machine-made rugs that combine durability, design consistency, and global market readiness.
1. What are machine-made rugs and how do they differ from handmade rugs?
Machine-made rugs are produced using automated looms and industrial weaving technologies, ensuring uniformity and repeatability. Unlike handmade rugs, which rely on artisan skill and manual labor, machine-made rugs are faster to produce, more affordable, and consistent in pattern, density, and pile height. They are ideal for bulk orders, commercial spaces, and modern home interiors.
2. Which types of yarn are best for machine-made rugs?
Common yarns include polypropylene (PP), polyester, acrylic, viscose, and wool blends. PP is durable and stain-resistant, ideal for high-traffic areas. Polyester offers softness and vibrant colors. Acrylic mimics wool for comfort, viscose adds luxurious sheen, and wool blends balance durability, softness, and cost. Choosing the right yarn depends on use, durability needs, and budget.
3. How does the weaving process affect the durability of a machine-made rug?
Durability depends on weaving density (tufts per square inch) and pile height. Higher density improves longevity and pattern clarity. Low pile rugs are firmer and easier to clean, medium pile balances comfort and durability, while high pile offers plushness but requires more maintenance. Proper loom calibration ensures consistent quality across the rug.
4. What finishing processes are applied to machine-made rugs?
After weaving, rugs undergo shearing to level pile height, backing with latex for stability, and edge binding or overlocking to prevent fraying. Additional surface finishing like brushing or steaming softens fibers, reduces shedding, and enhances texture, making rugs ready for homes, offices, hotels, or commercial spaces.
5. How is color applied to machine-made rugs and why does it matter?
Machine-made rugs use solution-dyed or space-dyed yarns. Solution-dyed yarns have pigment integrated into the fiber, providing excellent colorfastness and resistance to sunlight and cleaning. Space-dyed yarns create variegated, multi-tonal patterns for decorative appeal. High-quality dyeing ensures long-lasting vibrancy and uniform appearance across batches.
6. What quality control measures ensure machine-made rugs are reliable?
Rugs undergo inspections for tuft consistency, pile density, and color accuracy. Factories often combine automated scanners with human oversight. International standards like ISO 9001, Oeko-Tex 100, and ANSI/ISO testing are followed to guarantee safety, durability, and suitability for both domestic and global markets.
7. Why are machine-made rugs more cost-effective than handmade rugs?
Automated looms reduce labor costs and production time. Consistent processes allow bulk manufacturing without compromising basic quality. As a result, machine-made rugs are more affordable, accessible to a wider market, and ideal for residential, commercial, and large-scale projects.
8. Which types of machine-made rugs are best for residential, commercial, or hospitality use?
Residential: Medium-pile PP or polyester rugs for living rooms, bedrooms, and dining areas.
Commercial: Durable low-pile or high-density rugs suitable for offices and retail spaces.
Hospitality: Scalable production, consistent patterns, and durable yarns like PP or wool blends for hotels, resorts, and serviced apartments.
9. How should I choose a high-quality machine-made rug for export or bulk orders?
Focus on international quality certifications, consistent color and pattern replication, and durable packaging for transit. Verify yarn quality, pile density, and finishing processes. Reliable suppliers like Rug Legacy ensure that exported rugs meet global standards and arrive in perfect condition for sale or project use.
10. What are the most common problems with machine-made rugs and how can they be avoided?
Common issues include uneven pile height, color inconsistencies, and loose backing or frayed edges. These are prevented through precise loom calibration, strict dyeing protocols, backing reinforcement, and systematic quality inspections. Proper care and cleaning also help maintain durability and appearance over time.






